Gain access to personalized product screening, the best pricing, rewards, and more!
Most Effective Products
Bat Bugs vs. Bed Bugs
This page is a general guide that distinguishes between bats and bed bugs. Neither pest should be directly contacted, and furniture should not be moved until bed bugs are eliminated. To remove bats and bed bugs from your home, follow the links within this DIY guide and use the recommended products for complete control.
For some homeowners, they have an unfortunate association with bed bugs. Their ability to hide deep within interior walls and voids and multiply quickly makes them a hard pest to eliminate. However, despite homeowners' long-term battle with bed bugs, some homes may encounter another species of pest: the bat bug.
Like their relatives, bat bugs will hitch-hike into homes by attaching themselves to bats and then traveling off these animals into areas where they roost. Eventually, some bats can find their way into your home's chimneys, attics, and basements. Belonging to the same scientific family, Cimicidae, bat bugs, and bed bugs have key differences in habitat, food source, and some features.
An important distinction of bat bugs is their lack of insecticide-resistant mutations, likely because these pests have not been consistently exposed to pesticide treatments like bed bugs. Read on to learn more about bat bugs and bed bugs so that you can effectively eliminate them from your home by following the tips and products suggested throughout this DIY guide.
Identification
Before you can proceed with a treatment approach, you will need to know the physical differences between a bed bug and a bat bug. Misidentification can lead to using the wrong products or unnecessary treatments, which can be a waste of your time and money.
For a physical reference, examine the image above. On the left is the bed bug, and on the right is a bat bug. Due to their strong resemblance, a microscope or magnifying lens may be necessary.
Similarities
- Bed bugs are tiny, blood-sucking insects that range between 1/4 to 1/3 of an inch in length. Both the bed bug and the bat bug are brown and have a flat, oval shape, almost like apple seeds.
- Six legs that help the bat bug or bed bug to crawl from one location to another.
- Short, broad heads with a pair of antennae.
- After these pests ingest blood, their bodies become more elongated and reddish.
Differences
- The most noticeable difference between bed bugs and bat bugs is that the bat bug has longer fringe hairs on its body and is closer to its head than the bed bug.
Habitat
Though most people will be unable to tell bed bugs and bat bugs apart by looks alone, it's easier to distinguish the two by observing their different habits and habitats. Bed bugs and bat bugs both feed on blood from warm-blooded animals.
While bed bugs prefer to feed on people, bat bugs prefer to feed on bats whenever possible. They will feed on other animals if necessary, but bat bugs will not be able to reproduce without bats.
Bat bugs often find their way into homes when bats have nested in attics, wall voids, chimneys, or other secluded areas. Unlike ticks and fleas, bat bugs will travel away from their hosts to hide in cracks and crevices near where the bats roost. If the bats were absent for a long period, the bat bug would travel from their hiding spots to feed on any other animals they may be able to find.
In contrast to bat bugs, bed bugs infest lower ground areas such as mattress tufts and folds, bed frames, behind picture frames, underneath and inside electronics, underneath furniture, or behind electrical plates. Since bed bugs are small, they can travel to and from each room through shared ventilation and wall spaces. When looking for bed bugs, look for any blood stains, droppings, or smears on your bedding, blankets, pillows, and mattress.
Signs of Infestation
Bed bugs are usually most active at night due to how long people sleep in their beds, providing an easy meal. However, if you sleep during the day and not at night, bed bugs will emerge from their hiding spots to feed. Bat bugs are not particularly known for specific feeding times but can come out during the day or night to feed on your blood.
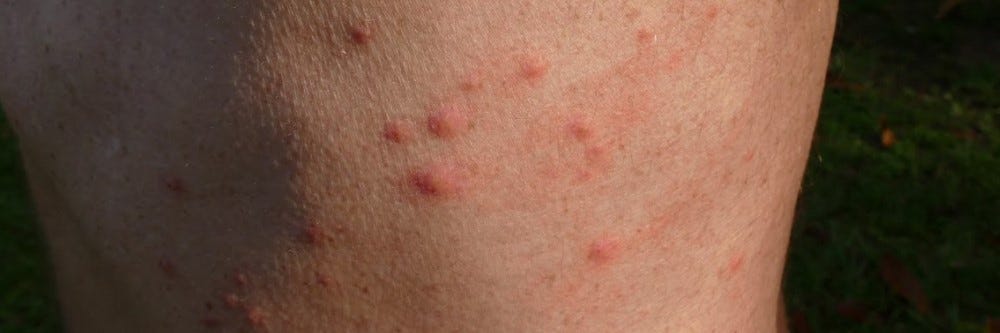
The most common signs of a bat bug infestation include seeing the pest or finding bites on your skin while sleeping. Unlike bed bugs, bat bugs will not remain near beds, furniture, or voids close to areas you frequently inhabit. Instead, these pests will return to where the previous bat colonies originally roosted. Once bitten by a bat bug, your skin may become inflamed, with swollen red marks. Sometimes, redness, itching, and swelling can occur like bed bug bites.
Like bat bugs, bed bug bites appear as small, red puffy bumps with red marks at the center. They can also appear as lines or groupings on the neck, arms, back, or trunk of the body, whereas bat bugs are not known for these patterns.
While searching for bed bugs, you can examine your bed or furniture for fecal traces (resembling dried blood with dark red or black coloration) or blood smears. Blood smears from bat bugs can be possible, as you could crush them in your sleep or through their travel activity.
Differences in Treatment
Bat bugs are fairly difficult to treat and control when bats are present. To get rid of bat bugs, you must determine where bats roost in your home. Otherwise, bat bugs will continue to thrive and potentially feed on you until its life cycle is complete.
We recommend using Supreme IT outside of your to eliminate food sources for the bat colony. When bats can no longer feed, they travel from your home to other areas.
Apply 1 fl. oz. of Supreme IT per gallon of water per 1,000 sq. ft. with either a handheld pump sprayer or backpack sprayer.
Once applied, this product will fight against 70 types of insects upon contact and up to 90 days after application. When bats are confirmed gone, close all voids and openings with caulk and copper mesh to prevent them from reentering your home.
Left with no other food sources, bat bugs can increase their feeding activity on homeowners. Although bat bugs feed on people, they will not be able to reproduce in this food source, eventually causing them to die out.
Though bat bugs cannot be controlled through most insecticides, bed bugs can. To get rid of bed bugs, the first step is to thoroughly wash your bedding. Transfer it into a large plastic bag and then into the washing machine. Use the highest heat setting on your washer and dryer to kill any adult bed bugs present. Do not put the bedding back until after treatment is complete.
Once the bedding has been washed, you will want to treat the infested room with products like Flex 10-10 and Gentrol IGR. Together, these will kill and control bed bugs in all stages of their life cycles in multiple environments.
The application rate for a severe bed bug infestation is to mix 6.4 fluid ounces of Flex 10-10 into 1 gallon of water. Spray just the mattress tufts, edges, seams, and folds.
Then, mix 1 fluid ounce of Gentrol IGR into your solution to treat 1,500 square feet. Once combined, spray the bed frame, box spring, furniture, closets, flooring, and baseboards.
Use a flushing agent like Pyrid Aerosol to remove bed bugs hiding in tight cracks or crevices.
For spots where liquids are ill-advised, like behind the electrical outlet, D-Fender Dust will kill and control insects that attempt to cross its dry barrier.
Apply 2 to 3 puffs with a handheld duster to thoroughly coat the application area. Once the room has been treated, we recommend using mattress and box spring encasements to stop the infestation from spreading further. For accurate product application and bed bug control, we recommend following our bed bug control guide.
Key Takeaways
What Are the Differences Between Bed Bugs and Bat Bugs?
- Bat bugs and bed bugs are strikingly similar in appearance, with the exception that fringe hairs along the body and close to the bat bug head are longer than bed bugs'. Another noticeable difference is that bat bugs do not stay close to people like bed bugs but will return to elevated voids, cracks, and crevices. These areas are often adjacent to where current or previous bat colonies roost.
Can Bat Bugs Survive on People
- Bat bugs may live up to one year in people's blood, but they cannot reproduce, leading to an eventual decrease in population.
How to Prevent Bat Bugs From Invading
- To prevent bat bugs in your home, you will need to apply Supreme IT to deter food sources for bats and seal cracks, crevices, and voids with caulk and copper mesh.