Buckthorn Control
Most Effective Products
Buckthorn Control: How To Get Rid of Buckthorn
Buckthorn, also known as European buckthorn or glossy buckthorn, is a tall, shrub which was introduced to North America in the early 1800s. It was brought to the country initially as an ornamental shrub, primarily to serve as hedges. However, this woody shrub was quickly discovered to be a hard to control pest which could thrive in a variety of conditions and on both land and near bodies of water.
Buckthorn is also able to thrive wherever established because of the fact it has few predators. Most animals and insects don't like to eat buckthorn which allows it to grow and spread without issue. Combine this fact with its plentiful seed production, and it's not hard to see how it can very quickly establish itself and come to dominate wetlands, savannas and other natural areas.
If you have buckthorn on your property, this DIY guide contains all you need to remove buckthorn quickly, efficiently and at an affordable price.
Identification

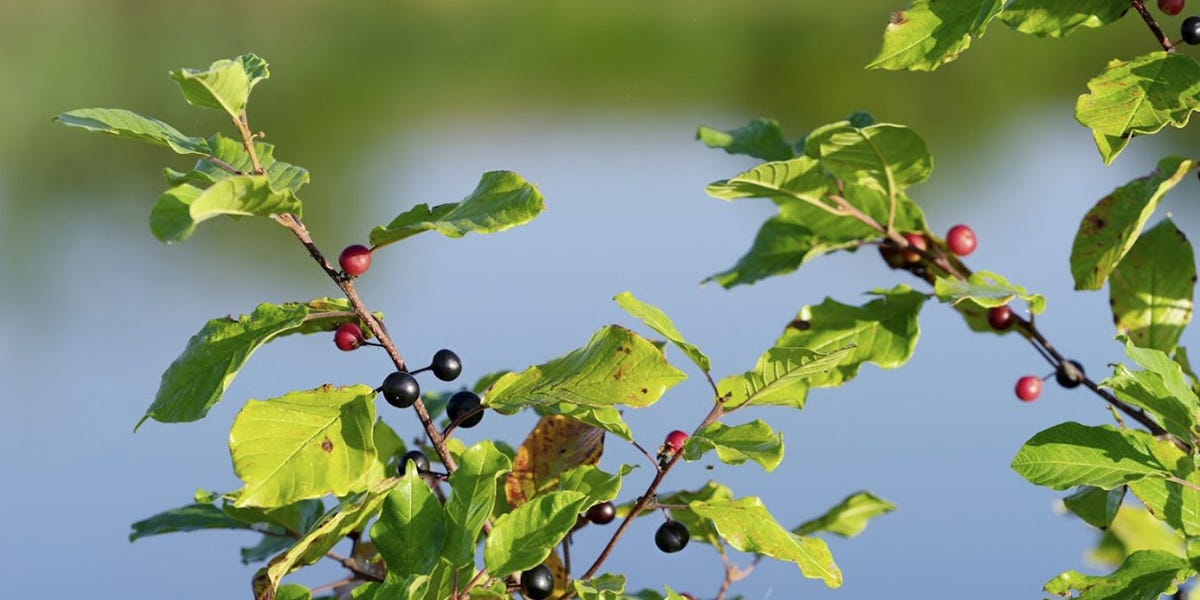
Buckthorn is a shrub or small tree which grows up to 25 feet feet tall in an oval form within wooded areas and near shorelines and other bodies of water.
Typically, it has glossy leaves that are smooth, toothless, and have 8 or 9 veins that radiate outward from a central mid-vein. Leaves stay green late into the fall after most other trees have shed their leaf canopy, making glossy buckthorn easy to identify at this time of the year.
Small, greenish-white, five-petaled flowers are produced in clusters near the base of the leaf stalks along the branches. Flowers consist of both male and female parts. Buckthorn can produce numerous purple-blackish berries that help to spread this invasive foliage in a short time span and even remains a problem after it has been removed.
Use the image above and our description to help you in properly identifying buckthorn on your property. If you get stuck, contact us via email with a close up picture of the plant and we will help you to properly identify the plant.
Inspection

Where to Inspect
Inspection should not be too difficult because if you have a buckthorn problem, it will be very apparent. Buckthorn are an invasive oval shaped brush that will form in undisturbed areas such as thickets, shaded areas, abandoned fields, around or near the base of trees, and areas with small trees or brush.
What to Look For
Examine the plant to determine what stage of growth is it in. In younger or mature buckthorns, they will be one of the first plants to turn green in spring and keep their green coloration late into the fall season.
During the spring, buckthorn will begin to sprout oval-shaped leaves with veins that connect towards the main stem of the leaf. In younger buckthorn plants, they will have a dull shiny gray wood with corky projections and little speckling marks. Additionally, younger buckthorns will have small, flowers amongst its leaves until June.
In more mature buckthorns, you will see purple or black berries surrounding the plant on the ground or hanging from their branches, usually this is between August and September. The bark will appear brown with elongated silvery cork projections that often mistake it for cherry or plum bark.
Whether young or mature, all buckthorns will have a needle-like thorn at the end of the stem. The needle-like thorn will be surrounded by two terminal buds that imitates the appearance of a buck hoof print.
Treatment
Make sure before you spray herbicides to have on the proper personal protective equipment (PPE) in the form of gloves, long-sleeve shirt, long-sleeve pants, closed-toe shoes with socks, safety glasses, and a respirator mask. Our top recommendations of herbicides to control is Triclopyr 4 Brush Killer.
What you choose depends on your budget but the active ingredients contained in these products do a great job of control. Mix the herbicide in a pump or backpack sprayer according to the label directions.
Step 1: Cut Buckthorn Down From the Base

For young buckthorn plants, use a set of heavy-duty pruners to cut the stems as close as possible to the base. This applies for older buckthorns, with the exception that you would use an saw or tree and shrub shears. Both of these methods will help to cease buckthorn growth and eliminate the spread of buckthorn via its berries seeds.
Step 2: Spray Herbicide on Cut Stems and Trunk

Triclopyr 4 Brush Killer is a systemic herbicide that works to eliminate brush such as buckthorn to its roots. Apply Triclopyr 4 Brush Killer to the base of the buckthorn plant and parts of the plant that have been cut.
A standard application of Triclopyr 4 Brush Killer is 2 to 6 oz. of product per gallon of water per 1,000 sq. ft. For large volumes of stumps, mix Triclopyr 4 Brush Killer into a sprayer at a rate of 20 to 30 gallons of product with an oil-based product (such as Methylated Seed Oil) to make 100 gallons of spray solution.
On forestry use sites, do not apply more than 6 lbs. of product per acre per year. On use sites that may be grazed, including right-of-ways, pasture, fence rows, and range-land, do not apply more than 2 lbs. of product per acre per year.
Fill a pump or backpack sprayer halfway with water, then measure the appropriate amount of Triclopyr 4 Brush Killer, and then fill the rest of way with the remaining half of the water. Secure the lid and agitate until it is evenly mixed.
Prevention

After buckthorn has been eliminated or is in the process of wilting, you may use a rake to remove as much of the dead plant and its berries from the ground as possible.
This will prevent an accumulation of dead plants and spread of buckthorn across your property helping to keep your turf clear and increase desired vegetation growth.
Key Takeaways
What is Buckthorn?
- Buckthorn is an invasive species of weed that can overtake land and areas surrounding water areas.
What Products to Use For Buckthorn?
- Triclopyr 4 Brush Killer does a great job in eliminating buckthorn.
How to Prevent Buckthorn Reinfestation.
- Regular monitoring, preventative applications of herbicides and adding a regular lawn-maintenance such as raking to your property are the best tips for preventing buckthorn.